Business intelligence (BI) was not invented yesterday. Coined in 1865 by Richard Millar Devens in relation to a banker who gathered market data before his competitors did, it has gone through a tremendous evolution since then. Modern businesses operate in the “data explosion” era, when more data is being created than ever before. Think about the complex networks of IoT devices that send real-time operational data from smart factories, the huge amounts of unstructured data that come from social media, and the core transactional data that is stored in CRM and ERP systems. The amount and complexity of this constant flow of information is growing very quickly, with data becoming the new fuel.
No surprise that the Business Intelligence and Analytics Market is going to double in the coming years, from $34.04 billion in 2024 to a projected $65.14 billion by 2032, which is an 8.45% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR).
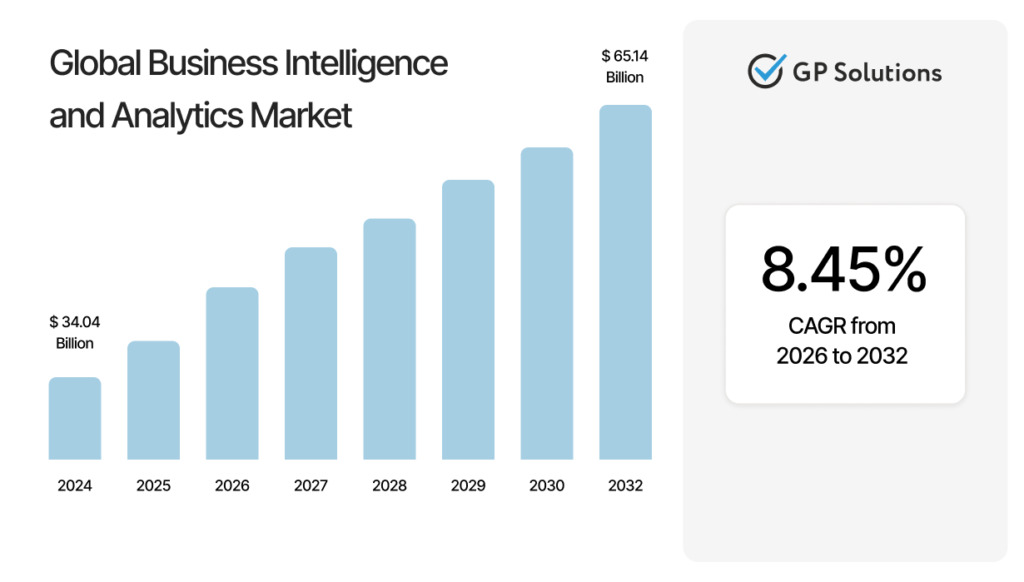
Source: Verified Market Research
Despite the obvious potential, many companies still let vast amounts of raw data lie idle and untapped, missing out on their most valuable asset. The competitive advantage will go to those who don’t just collect data but also use it to make decisions that are both prescriptive and predictive. And considering how much data is generated daily, the demand for data management solutions is on the rise. But what are the latest business intelligence industry trends? What’s next for BI?
If you’re a C-level executive or strategist who wants to go beyond the descriptive nature of traditional BI, this article will fill in the knowledge gaps for you. We will look at the major changes and trends that will shape the BI landscape in the years to come. We will also show you how to turn your raw business data into strategic benefits with a long-lasting effect.
What Is Business Intelligence, and Why Do They Use It?
Today’s business intelligence is an essential practice of collecting, organizing, and analyzing huge amounts of business data to yield actionable insights that directly contribute to strategic plans and improve daily operations. Static reporting still serves its purpose in cases when your company needs to adhere to regulatory compliance or generate end-of-year financial reports, but BI platforms have gone beyond this descriptive approach. They provide business users with the ability to easily access and analyze a wide range of data, including historical, real-time, in-house, and third-party data, as well as unstructured data from sources like social media. Business intelligence and analytics transform raw data from a passive asset into a unified tool that helps make decisions based on predictions, which directly affects the direction and performance of the business.
Ultimate Guide to Business Intelligence

And it comes with multiple strategic benefits:
- Clearer reporting
- Decisions based on data insights
- Consolidated data
- Solving problems on the spot
- Real-time monitoring against benchmarks
- Faster decisions
- Adjusting strategies to changing conditions
- Digitized analysis processes
- Immediate access to integrated customer insights
- Self-service access to critical data granted to non-technical users
- Real-time problem identification and resolution
- New revenue/business opportunities
Typical BI Process within an Organization
Implementing a BI solution within your organization requires understanding of the vital BI steps.
| Step | Purpose | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Identification and Selection of Data Sources | You identify the data you want to review and analyze. | Sources involved: data warehouse/lake, cloud, Hadoop, CRM/customer records, inventory, sales, industry statistics, supply chain, marketing/promotions, social media |
| Data Collection | You collect and clean data from multiple sources. | Manual collection in a spreadsheet, automated ETL software |
| Analysis | You inspect data for patterns, trends, or deviations. | Processes/tools involved: data mining, data modeling, data discovery, ML, NLP, OLAP, predictive analytics, prescriptive analytics |
| Output and Visualization | You get visual representation of your data (graphs, dashboards, maps, etc.) with the possibility to inspect its various levels (drill-down, drill-through, drill-up features). | Tools involved: Tableau, Cognos Analytics, Microsoft Excel, SAP, etc. |
| Actionable Insights | You create an action plan by comparing historical data to your KPIs. | Outcome delivered: better customer experience, redefinition of target market, focus shift in market plan, changes to or complete overhauls of your processes, stricter security, product redesign, adjusted supply chain, revised pricing strategy |
Business Intelligence Trends
Now that we have made sure we are on the same page regarding why and how BI is implemented by companies around the globe, it’s high time we get down to scrutinizing the latest trends in business intelligence that are going to define the tech landscape in the near future.
Trend 1: The Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Algorithms
You wouldn’t expect us to avoid AI, would you? This invention has long passed the stage of questionable hype and grown to become a proven driver behind companies’ efficiency. Investment is quickly going from exploration to implementation. A recent IBM study found that 66% of executives say they are already seeing productivity gains from AI and expect to see substantial returns on their investments within the next year.
Faster Insights and the Functionality to Predict Things
The newest developments, especially in GenAI, are tearing down old data bottlenecks. AI-based systems take over the tedious work of data preparation by replacing manual data cleansing, transformation, and integration with faster, more accurate methods. This basic automation accelerates your ability to analyze vast amounts of data and get immediate insights from multiple sources.
ML algorithms, in their turn, are what makes the move from static, descriptive reporting to predictive and prescriptive analytics possible. ML can predict business outcomes with remarkable accuracy by constantly processing huge amounts of historical and real-time data. It can also trace even the slightest changes in customer behavior and predict market trends that are likely to change. This power to predict the future enables companies to go from reacting to proactively shaping their future.
Democratization and Speed of Decision Making
AI can provide access to advanced analytics for everyone, which is probably the most effective change it can bring about. The technology fills the gap between advanced data science and the needs of regular business users.
- Self-Service Insights: AI tools now have Natural Language Processing (NLP) interfaces. This means that non-technical teams can just ask the BI system questions through a chatbot, for instance, and the chatbot will automatically create the complicated queries (like SQL) that are needed. For more on self-service BI, please consult the next chapter.
- Automated Discovery: With upscaled insights, users only need to choose a data source and a focus variable (like revenue) for the program to automatically analyze the datasets. The algorithm quickly returns a full analysis that includes forecasts, value drivers, correlations, and finding outliers.
This level of automation and personalization speeds up decision-making notably. AI now does what a data scientist used to do, ensuring all authorized business users have immediate access to high-quality, actionable intelligence and strengthening a truly data-driven culture.
Trend 2: Self-Service BI Applications and Democratization of Data Expertise
BI needs both the freedom to explore and the rules to keep trust safe. For a long time, the idea of Self-Service Business Intelligence (SSBI) seemed like the ultimate quest of analytics. That concept has entered the list of top business intelligence industry trends, as the vision is finally coming true today, which is a big shift in how organizations will operate.
In the SSBI model, the central IT team still takes care of corporate data (security, accuracy, and access), while giving non-technical users direct, independent access to information they need. This fundamental shift provides data teams in every part of the company with the ability to use BI tools and conduct complicated analysis with no need for a technical background and no need to wait in line for the tech department to process their query. This makes every team member an active participant in the analytics process.
Trend 3: Natural-Language Queries (NLQ) and Conversational BI
In a world where we expect to “Google” our enterprise data, Natural-Language Query (NLQ) is one of the defining BI industry trends in user interaction. NLQ changes BI by enabling you to ask complicated analytical questions in simple, everyday language. This means that as a user you don’t need to know how to use SQL or have other specialized skills. This new approach is making data much easier to understand and employ, which is causing a huge increase in its use.
The Semantic Layer’s Strength
The concept of Conversational BI is very compelling against the backdrop of other business intelligence industry trends; however, querying in plain language is far from being that simple, particularly when various teams employ distinct jargon (e.g., one team refers to “customer churn,” while another uses “attrition rate”). NLQ quickly fails without consistent terminology, which leads to doubtful results.
This is when the semantic layer becomes unavoidable. The semantic layer provides NLQ systems with the essential context they need to return accurate, reliable answers by establishing a centralized, governed model of all business logic and metrics. Also, as advanced AI agents powered by technologies like the Metric Context Protocol (MCP) become more common, these semantic models are not only powering dashboards, but they are allowing machines to think, act, and speak the exact language of the business.
How Use Cases Set a New Standard
Natural Language Processing (NLP) stands behind two major use cases:
- BI data assistants are built into BI platforms, just like smart assistants you might already encounter. AI processes a question typed in human language and sorts, filters, and creates analytical insights as a direct answer. This feature makes data analysis available to everyone, with non-technical users obtaining quick, self-service access and cutting down on the time to get products to market.
- Sentiment analysis: NLP expands the value of opinion mining, which means looking at a lot of unstructured text data from sources like social media, emails, and surveys to figure out the emotional tone (positive, negative, or neutral). This ability lets companies quickly get important information for product development, brand positioning, and customer pain points on a large scale, which directly affects their customer experience strategy.
Trend 4: Agentic AI
Agentic AI is the next logical step forward for AI in business intelligence. These mechanisms can work on their own to reach certain goals without constant human help. There is a big difference between them and static, rule-based models. Agentic AI uses the reasoning power of Generative AI to make decisions and carry out actions, but its capabilities do not end with content creation. This technology has supercharged reasoning and advanced execution capabilities that will greatly improve how humans and machines work together in 2026 and beyond.
Trend 5: Explainable AI (XAI) and Transparency in BI
In the age of AI, you need to give and get explanations. When a complicated model suggests a crucial course of action, leaders, especially those in regulated industries, must comprehend the reasoning behind it. Explainable AI (XAI) is at the center of the conversation because people need more and more clarity. XAI uses certain methods to help people understand the results and outputs of ML algorithms, which builds trust and control. The semantic layer is very important for this because it keeps track of the business logic, data lineage, and definitions for each insight. This openness is necessary for checking, improving, and making sure that automated recommendations are in line with the company’s long-term goals.
Trend 6: Governance of BI Use
With Self-Service BI among the major trends in business intelligence, more business users can access data directly. Because of this, data security and privacy have become even more critical because of rising cyber threats and strict rules like GDPR and HIPAA. Data governance is now one of the most pressing aspects that businesses using BI need to think about.
Vendors, in their turn, are adding specific compliance features to their platforms in response to the rise of cyber crimes. New technologies, such as analytics catalogs, are also being added to the game. These create a single place for users to find the BI dashboards and reports that are most relevant to them. This approach makes sure that the entire decision-making process is well-managed. Here, the Semantic Layer plays a vital role again because it makes compliance easier by enforcing access control and row-level security at the logic layer throughout the entire analytics ecosystem.
Trend 7: Data Quality Management
High-quality data is what makes strategic decisions possible. As AI and ML become more indispensable to BI, the accuracy of their models depends on how consistent and reliable the source data is. In short, you can’t build intelligence on top of chaos. Bad data means bad choices and missed chances.
As a result, companies are pouring huge investments into AI/ML-powered data quality tools that use predictive analytics to fill in missing values and large language models (LLMs) to make sure that product names are consistent across all fields.
One noteworthy development within this trend is the focus on data pipelines, which are not static but dynamic and adaptable sources for analytics. Pipelines let you set different quality standards depending on the use case. This makes it easier to clean and conform data than traditional ETL. In the end, the Semantic Layer protects data by enforcing standards and keeping these pipelines’ integrity, which greatly improves the accuracy of the model.
Trend 8: Data Warehouse Modernization and the Rise of Data Lakehouses
As AI and data science applications are gaining more spread, you need to update data stores all the time. Data lakes started out as places to store raw data, which was then used to create structured, cleaned data for the traditional data warehouse. Analyzing the current BI industry trends, we clearly see that a new type of architecture is emerging: the Data Lakehouse. This design combines the flexibility of a data lake with the speed and strong data management of a warehouse. The Data Lakehouse is very critical for BI users because it gives them access to more data and makes it easy to add advanced processes like machine learning to the main BI and analytics workflow.
Trend 9: Low-Code and No-Code App Development
As more people learn how to use data, the need for analytics tools that help people make data-driven decisions in specific situations outside of traditional desktop applications (like for sales or maintenance) grows. To make these kinds of apps, you used to need BI developers. Low-code and no-code (LCNC) features built into BI platforms have made this process available to everyone. LCNC environments do away with the need for high-level development skills, allowing business users to independently create and deploy custom, lightweight BI apps. These apps can run on any device, including desktops, the cloud, and mobile devices. This means that every user in the organization can access useful BI data.
Trend 10: Embedded Analytics
Embedded analytics is a big change from BI being a destination to BI being a part of a bigger system. This BI and analytics trend is all about adding BI features like interactive dashboards, reports, and data visualizations directly into operational apps like CRM systems, ERP systems, and customer service platforms. The strategic value is clear: it gives users useful information in the course of their normal work, so they don’t have to switch apps, and it helps them make decisions in real time.
There isn’t enough time to check numbers on five dashboards when a customer is on the phone. The data needs to be reliable and available right away. Semantic Layers make this possible by letting you query data in real time and at high speeds right in the operational tool without moving it.
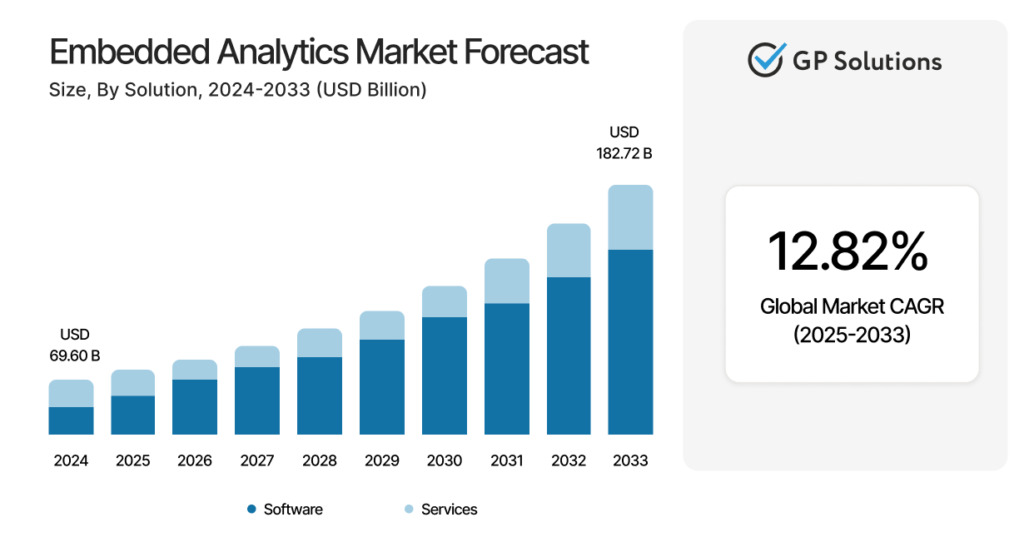
Source: Verified Market Research
The market impact shows how important this trend is, with the embedded analytics market expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.82% to $182.7 billion by 2033.
Embedding BI can help your business run more smoothly and make a lot of money. More and more businesses are putting analytics into their own products and selling them under their own name, which gives their customers more value. This method encourages teamwork and increases user adoption.
BI Use Cases
The technology can find its way into virtually any domain that handles data as part of its operations or as a subordinate process. We invite you to explore real-life examples of its application across industries.
| Sphere | Potential Manifestation |
|---|---|
| Travel and Hospitality | Analyzes real-time booking patterns and seasonal demand to execute dynamic pricing strategies, while consolidating guest feedback from all channels to improve service quality. |
| Customer Service | Unifies customer and product data, allowing service teams to access a single source of truth, resolve concerns faster, and improve first-contact resolution. |
| Finance and Banking | Consolidates customer histories and market data to assess organizational health, predict risks, and analyze performance (e.g., branch-by-branch) to identify investment opportunities. |
| Healthcare | Optimizes internal operations by enabling real-time, minute-by-minute tracking of critical inventories, staffing, and patient flows, while also powering patient-facing data portals. |
| Retail | Drives cost savings and efficiency by comparing performance benchmarks across all stores, channels, and regions from a single, unified dashboard. |
| Insurance | Provides clear visibility into the entire claims process, allowing insurers to identify service bottlenecks, improve outcomes, and reduce processing costs. |
| Sales and Marketing | Unifies data on promotions, pricing, and customer actions, enabling detailed segmentation and market analysis to plan targeted campaigns that boost sales and ROI. |
| Security and Compliance | Centralizes security and log data into a unified dashboard to rapidly determine the root cause of threats and simplify regulatory compliance reporting. |
| Statistical Analytics | Uses descriptive analytics to review organizational statistics, allowing leaders to spot emerging market trends and immediately uncover the root causes driving them. |
| Supply Chain | Provides worldwide data on a “single pane of glass” (SPOG) to speed the movement of goods and rapidly identify supply chain inefficiencies and bottlenecks. |
| Construction | Unifies disparate data from digital tech (AI, sensors, digital twins) into real-time, interactive reports, ensuring all decentralized teams work from a single source of truth. |
Why Some Companies Struggle with Business Intelligence and Analytics
Despite the obvious loads of benefits a company can get from implementing BI and data analytics into its processes, our experience shows that many leaders are facing considerable obstacles preventing them from becoming a data-driven business. The most widespread include:
The Lack of Data Skills
The lack of qualified professionals is a big problem for the market. More than half of companies around the world say they have trouble finding people with the right skills in data science, engineering, and BI tools. This deficit of skilled workers raises costs and slows down the rollout of BI solutions. A wider gap in data literacy among business users makes this even worse. Even with advanced tools, many workers don’t know how to read complex data, find useful insights, and use them well to make strategic decisions.
If you are looking for a specific skills set to add to your team, GP Solutions may fill in your gaps. Contact our team, and we’ll discuss your BI needs, analyzing how we can help you with your BI-driven transformation.
Difficulties with Integration and Data Quality
To get reliable results from BI, the focus needs to be on the quality of business data. A lot of companies have trouble with a fragmented data landscape, where information is stored in different silos and old systems. Adding new BI tools to this environment is a difficult and time-consuming task. Also, bad data quality, wrong, inconsistent, or missing information, guarantees wrong conclusions, which hurts the credibility of your BI project in its entirety.
High Costs of Implementation and Resistance from the Culture
The high cost of modern BI solutions is a big problem, especially for small and medium-sized businesses. This includes the high costs of software, integration, hardware that is needed, training all employees, and ongoing technical support.
Lastly, managing change in an organization is a real issue in many companies, especially large corporations with many years of existence. A lot of companies prefer to stick with tried-and-true manual processes. If executives don’t support or departments don’t buy into new BI tools, employees may see them as too complicated or a threat instead of an opportunity. This resistance, along with the possibility of different teams coming to different conclusions from self-service tools, can cause problems in the organization instead of a unified, data-driven strategy.
Data Is the Lifeblood of Your Company’s Future
From Agentic AI and Natural Language Queries to Embedded Analytics, the business intelligence industry trends that will shape BI in 2026 and beyond show that data is the lifeblood for a modern business. It’s no longer possible to passively report. Organizations that use these trends to turn raw data into a useful, predictive asset now have a competitive edge.
C-level leaders no longer need to ask if BI is necessary; they need to figure out how to put in place a strong strategy that guarantees data quality, governance, and flexibility. It’s hard to modernize a data warehouse or put in place a full-scale AI strategy, but the cost of not doing anything is even higher.
Need to build a data warehouse or maybe even a lakehouse? GP Solutions is an expert partner to help you get through this future. With us, you can start your BI transformation and turn these new trends into a real competitive edge. Just drop us a few lines, and we’ll contact you shortly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Business Intelligence (BI)?
Business Intelligence is an important part of running a business that involves gathering, organizing, and analyzing business data to find useful information. These insights directly shape strategic plans, improve daily operations, and turn raw data from a passive asset into a tool for making decisions based on what will happen in the future.
What are the main advantages of putting a BI strategy into action?
A modern BI strategy has many strategic advantages, such as:
- Making decisions based on data
- Bringing together data from all sources into one place to make it easier to find the truth
- Real-time monitoring lets you solve problems right away
- Speeding up the process of making decisions
- Finding new ways to make money and new business opportunities
- Giving non-technical users access to data on their own
What is the most important BI trend to look out for in 2026?
The most important trend is the combination of AI and ML. AI is being used to automate the preparation of complex data, make powerful predictive analytics possible, and run self-service tools like Natural Language Queries (NLQ), which let users “Google” their company data.
What does “Self-Service BI” (SSBI) mean?
Self-Service BI (SSBI) is a method in which the main IT team is in charge of keeping data safe and accurate, but business users who aren’t tech-savvy can access the data directly and on their own. They can do their own analysis and get information without having to wait in line for the tech department.
What does the term “Data Lakehouse” mean?
A Data Lakehouse is a new way to store data that combines the flexibility of a “data lake” (which holds raw, unstructured data) with the speed and management features of a “data warehouse” (which holds clean, structured data). Integrating advanced processes like Machine Learning into the BI workflow is very important.
Why do a lot of businesses fail when they try to use BI?
There are a few common reasons why companies have trouble with BI implementation:
- The Data Skills Shortfall: There aren’t enough qualified people who know how to do data science, engineering, and BI.
- Integration Problems: It’s hard to connect new BI tools to old, broken systems and data silos.
- Bad Data Quality: Data that is wrong, inconsistent, or missing can lead to wrong conclusions and a lack of trust.
- High Costs: The initial costs of software, integration, and training can be a problem.
- Cultural Resistance: Employees or executives who don’t want to change from old, manual processes.
How can my business make up for the lack of data skills so that BI can be used?
Our article states that a lack of qualified workers is a big problem for a lot of businesses. If your company has this gap, you can work with an expert team like GP Solutions to fill in the skills you need and help you with your BI-driven change.



















