Practically any action you make in the digital economy of today leaves a digital footprint, be it a customer click or a supply chain transaction. But for businesses out there, this unstoppable buildup of data has a dual nature. On the one hand, it’s an untapped goldmine. On the other, it’s a well-documented liability. A report from Seagate Technology from last year highlights that around 68% of data that enterprises have access to goes untouched. It would be wrong to qualify it as a missed opportunity only; it’s a substantial operational drag, a complex silo that takes up your storage and budget while you get little in return.
To outperform competitors, a business should care not so much about acquiring more data but rather about how you activate what you already have. The goal here is to shift from data being a passive byproduct to it becoming an active revenue driver. This fundamental change can be powered by business data analytics. As Peter Sondergaard, former Gartner Executive Vice President, once said, “Information is the oil of the 21st century, and analytics is the combustion engine.”
But what is business data analytics? True BDA is a strategic discipline that is intended to use data, statistics, and predictive algorithms to equip you with better knowledge of your business operations and empower your decision-making. Yet it’s not about producing elaborate reports or impressive dashboards. BDA replaces guesswork and intuition with a strategy based on evidence. A survey from the Harvard Business Review shows that data and AI leaders beat their peers across operational efficiency, revenues, customer loyalty, and a range of other key business metrics.
GP Solutions has prepared this guide for those of you who want to go beyond the storage level. We are going to cover the principal concepts behind data analytics for business, provide a roadmap for its implementation, and present a few examples of how BDA converts stored data into an asset. Our goal is to lay the informational foundation so that you could lead your company in the BDA integration journey. Let’s roll in!

We can help you roll out data analytics within your company. Just leave us a note.
The Four Levels of Knowing: Types of Business Data Analytics
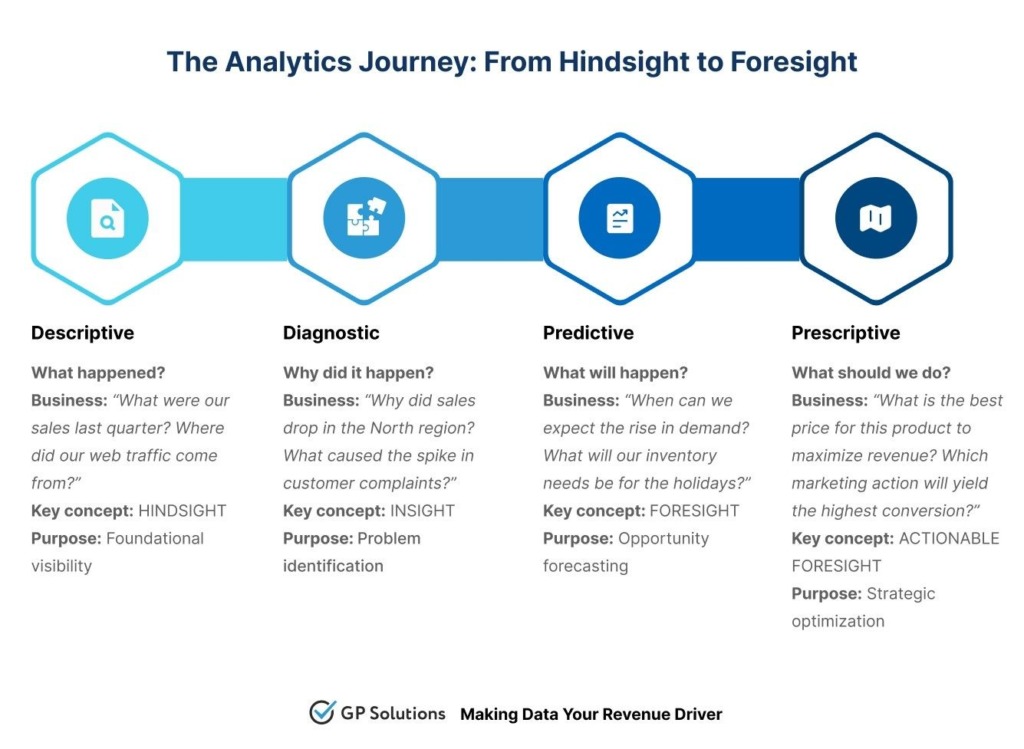
To make the best of your data, you need to be aware that data analytics in business isn’t a one-time, straightforward process. This process usually consists of four distinct steps, which we refer to as analytics types. To build a powerful analytics roadmap for your business, first you need to understand this progression.
Descriptive Analytics: What Happened?
This type lies at the core of all data analytics for business and is the most common use case. Descriptive analytics feeds on historical data to summarize information and provide a clear picture of past events.
It is when you are looking at the sales dashboard saying that Q3 revenue was down 5%, or a web report where you understand that your new marketing campaign lured 20,000 new visitors, or a presentation from the HR department with detailed turnover rates by unit. It depicts what happened in more detail but lacks the explanation why.
Diagnostic Analytics: Why Did It Happen?
Once you know what happened, the next logical step is to find out why. Diagnostic analytics is the process of scrutinizing your data to find out what caused things to happen in the past.
For instance, a retail business might use diagnostic analytics to figure out why sales are down. They might uncover that this negative dynamic was due to a 30% drop in the area where the competitor was driving an aggressive marketing campaign. Or a manufacturer could use it to find out that intermittent machine failures are linked to a software update introduced recently, thus preventing bigger problems from happening.
Predictive Analytics: What Is Likely to Happen?
This is where business data analytics starts to provide you with information that can impact your future. Predictive analytics uses historical data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning to guess upcoming developments. This feature is in hot demand, with the predictive analytics market expected to grow from $22 billion in 2025 to more than $147 billion by 2034.
Among what we already have, a good example is UPS’s ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation). This AI-driven system consumes traffic, weather, and delivery commitment data to devise the best route for each driver. ORION saves the company about 100 million miles and 10 million gallons of fuel each year.
Prescriptive Analytics: What Should We Do?
This is the most advanced and promising type of analytics. Prescriptive analytics results from predictive analytics by outlining specific steps a business should take to get the results it wants or mitigate potential issues in the future. It doesn’t just show you what’s going to happen; it helps you make it happen.
The Netflix recommendation engine is a great example here. Not only does it predict which movies you’ll like, but it also suggests specific titles on your homepage to keep you engaged and coming back. Airlines also use prescriptive models for dynamic pricing by automatically changing ticket prices in real time to get the most revenue based on expected demand.
If you get the essence of this progression — hindsight, insight, foresight — and manage to build your business data analytics strategy accordingly, your organization will be able to navigate all the data at hand at max capacity.
The Blueprint for Implementation: How to Build a Data-Driven Organization with Data Analytics for Business
It’s great to accept the power of data analytics for business; another thing is to get it to do the job within your organization. Many projects fail not because of the lack of some tech, but because they lack a relevant implementation strategy that covers all the layers and stages required to switch from a conventional business model to a data-driven one.
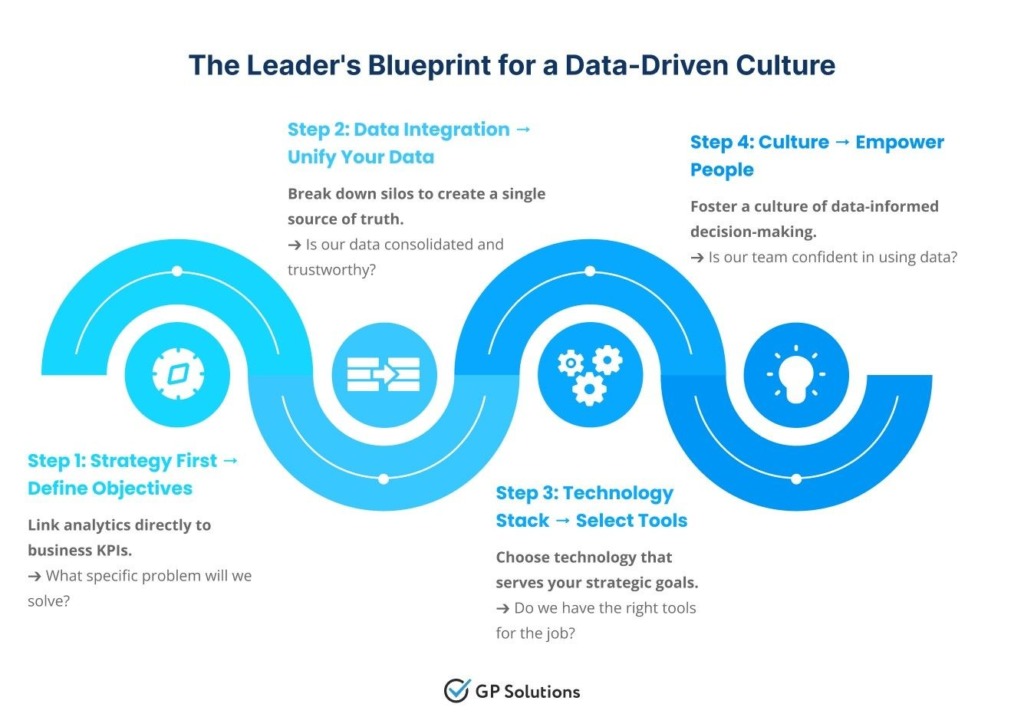
GP Solutions has devised a practical, four-step blueprint to ease your journey toward this mindset switch.
Step 1: Begin with Business Objectives, Not Technology
It’s really easy to get lost in tech tools available for businesses today, but you must resist this excitement and temptation and first define which problems you want to tackle. A business data analytics strategy must be rooted in your primary business goals. Before you opt for a particular software solution, answer the following questions:
- What are we trying to solve or to fix (e.g., reduce customer churn, optimize supply chains, increase customer lifetime value)?
- Which KPIs are going to assess our success?
- Which decisions will this data transformation empower us to optimize?
If you start with a strategy, your investment in data analytics for business will not be an expensive experiment but will be directly linked to measurable ROI.
Step 2: Unify Your Data by Breaking Down Silos
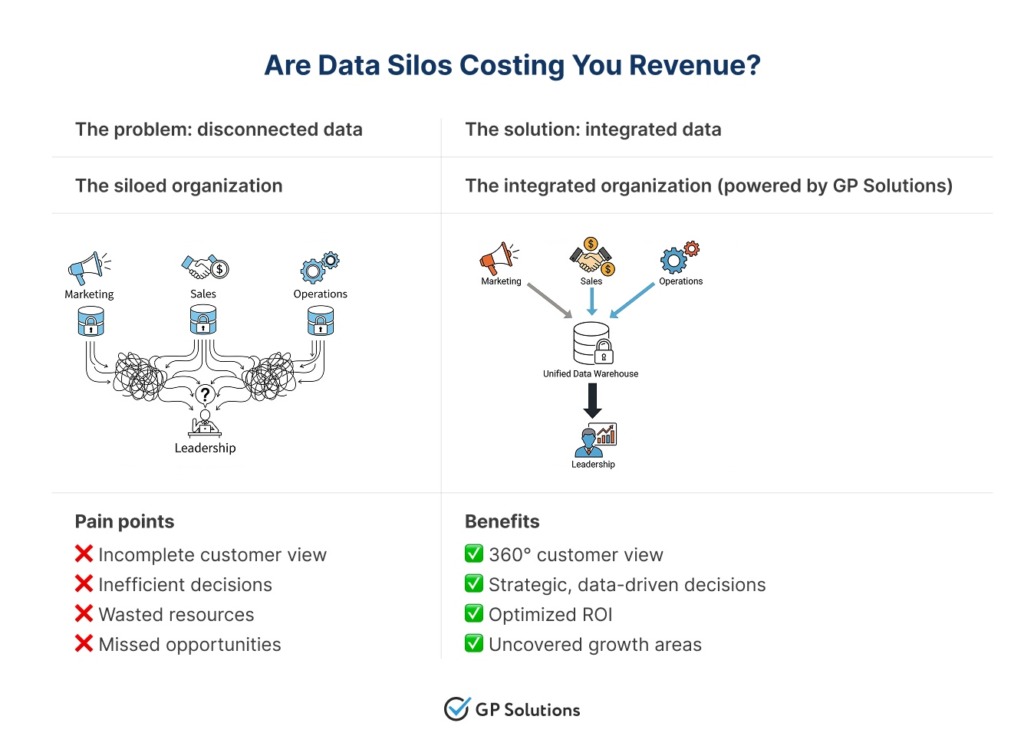
At GP Solutions, we have worked with all kinds of enterprises — from startups to large companies — and can expertly say that data fragmentation is the biggest technical hurdle for many established businesses. Most probably, you store precious information in CRM, ERP software, marketing automation platforms, financial databases, and legacy systems. You can’t get a full, 360-degree view of your business or your customer when data is stored in these silos.
This is why it is important to establish a “single source of truth.” To place all of your information into a central data warehouse, you need to set up reliable data pipelines and smooth integrations. This is a difficult task that requires a lot of technical knowledge, since standard connectors don’t always work well with custom or legacy systems. Getting past this problem is the first step to getting any use from analytics.
Step 3: Select the Right Technology Stack
Now that you have defined goals and unified all the data you need, you can choose the right tools. As a rule, there are several layers in a modern business data analytics stack:
- Data storage: Cloud-based data warehouses, such as Google BigQuery, Amazon Redshift, or Snowflake, offer storage with scalability and flexibility at core.
- Business Intelligence (BI) platforms: Tools like Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, and Looker let your teams visualize data, make interactive dashboards, and produce reports.
- Advanced analytics tools: This suite may include specialized machine learning platforms or custom-coded algorithms for predictive and prescriptive analytics.
The goals you set in Step 1 will help you choose the right stack for your business.
Step 4: Cultivate a Data-Literate Culture
Technology alone is not enough to raise and grow a data-driven company. The last step, and maybe the most important one, is to create a culture of data literacy. Accenture did a study and found that only 21% of the world’s workers are completely sure of their data literacy skills, even though there is a high demand for them.
To build this culture, you need to give employees at all levels the power to read, understand, question, and make decisions based on data. It needs support from top executives, regular training, and celebrating data-related wins. You have built a truly data-driven organization when everyone on your team is encouraged to ask, “What does the data say?”
“What’s in It for Me?” — How Data Analytics Helps Businesses
The ideas behind data analytics in business may be encouraging, but for any business leader, the bottom line is the most important consideration. A viable BDA strategy is no intellectual exercise; it’s what keeps an organization healthy and brings it money. The benefits can be traced in four main areas, where data transforms from an idle resource to a revenue driver.
The Fundamental Benefits of Business Data Analytics
Better decision-making: BDA substitutes intuition and speculations with empirical evidence at its core. It will provide you with a clear, factual basis for making strategic decisions, such as entering a new market, developing a new product, or allocating resources. Such an approach greatly lowers risks and raises the chances of success.
Better operational efficiency: Business data analytics enables leaders to look at every process in their business through a microscope. Companies can save a lot of money and get more done by finding bottlenecks, predicting failures, and making complex logistical chains more efficient.
Better understanding of your customers and personalization: In a crowded market, Know Your Customer (KYC) practices provide you a competitive edge. BDA lets you go beyond general demographics and look at individual behaviors, guess needs, and offer your audiences highly personalized products and experiences that make them more loyal and increase their lifetime value.
Proactive risk and opportunity management: There are always new risks and evolving opportunities in the business world. Companies can stay ahead of their competitors by going into the nature of market trends, customer sentiment, and their own performance data to see where things are going, what threats they might face, and where they can find new sources of income.
Real-World Use Cases: Analytics in Action
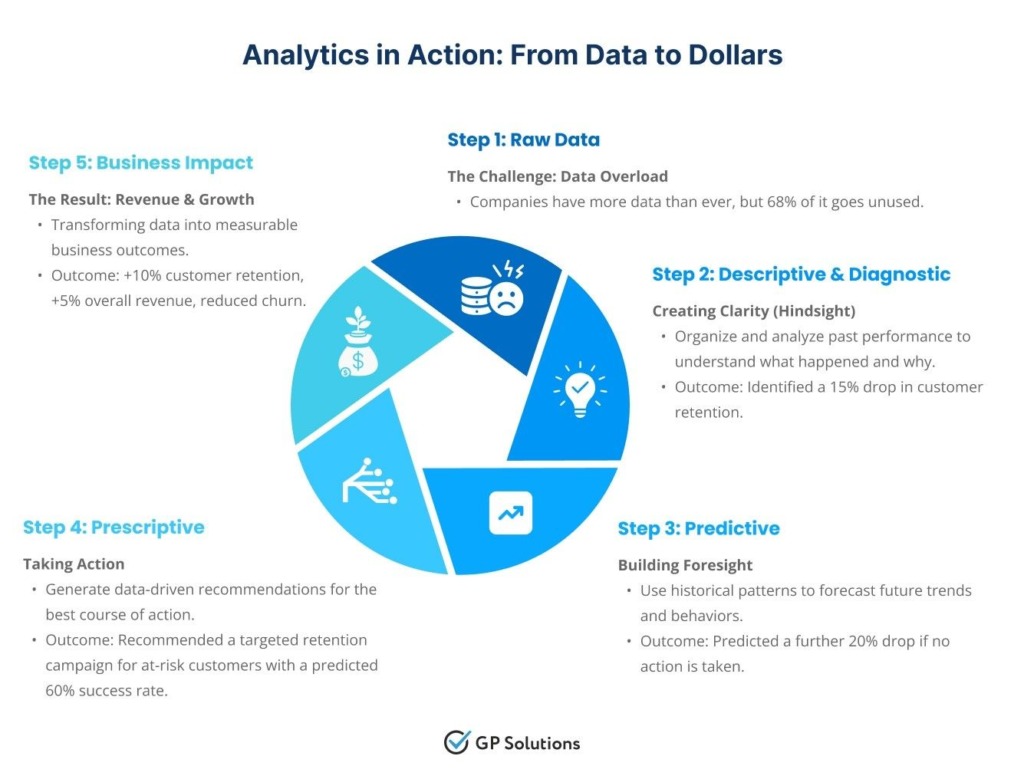
Knowing is great, but only seeing is believing. GP Solutions has summoned a few examples of how world-scale companies are already using data analytics for business.
Retail and Supply Chain: Walmart’s Inventory Mastery
For a retailer of its size, managing inventory is a challenging task, and even a small improvement of one percent can mean billions of dollars in future revenue. Walmart uses an analytics system called Retail Link which provides suppliers with up-to-date information on sales forecasts, inventory levels, and product performance in stores. With such data transparency, suppliers can plan their production and distribution ahead of time, which reduces the chances of stockouts and overstocks. Walmart can accurately predict demand by looking at point-of-sale data in real time. Such information helps the company improve its supply chain, lower carrying costs, and make sure that products are on the shelf when customers want them.
Manufacturing: Continental’s Predictive Quality Control
In manufacturing, waste, also known as “scrap,” exerts major influence on profitability. To predict scrap in its complicated tire-making process, the tire company Continental introduced machine learning. Their predictive analytics model can tell when a batch of material is about to fall outside of strict quality tolerances by looking at thousands of variables from production sensors in real time. It lets production engineers make changes right away, which cuts down on waste and speeds up production. It is a great example of how predictive analytics can answer a multi-million-dollar question.
Travel and Hospitality: Dynamic Pricing in the Airline Industry
The travel industry, one of the focus industries of GP Solutions, represents a dynamic landscape for the implementation of data analytics in business. Delta and other airlines have gone far beyond fixed seasonal pricing. They use advanced revenue management systems that look at many real-time factors, such as how many people want to fly on certain routes, how much their competitors charge, booking velocity, major events, and even how customers browse. Using these predictions, prescriptive algorithms automatically change ticket prices for every flight to make the most money, making sure that every seat is filled and taking advantage of last-minute demand. This flexible plan is an important part of how airlines make money today.
Healthcare: Predicting Patient Risk to Save Lives
Predictive analytics has a direct effect on people in the healthcare field. Health tech providers are working on models that scrutinize electronic health records (EHRs) to predict patient outcomes. Providers can take action ahead of time by making personalized care plans for patients who are at high risk for conditions like sepsis or being readmitted to the hospital. This not only saves lives and improves treatment plans, but it also spares a lot of money on operations by avoiding expensive emergency procedures and readmissions.
The above examples are clear evidence that the application of business data analytics is not limited to a few selected industries. The strategic approach to its implementation into your operations and data systems will save you from the morass of chaotic data and turn it into a money-friendly partner.
The Future Is Data-Driven: Latest Developments
Data analytics for business doesn’t just unlock insights and make things easier for you; it’s the start of a bigger transformation. To establish a strong market presence, leaders need to use analytics to solve today’s problems and make plans for the future. This means revamping how your IT department works, redefining ROI, and keeping a close eye on the new technologies that are expanding their value across the tech community.
The field of business data analytics is changing rapidly. We have singled out some trends that are definitely worth your attention:
The Rise of Generative AI and Augmented Analytics: Generative AI and other technologies are changing the way we work with data at a basic level. The trend of “Augmented Analytics” automates a lot of the effort that goes into data preparation and insight generation. Soon, any of us will be able to ask complex questions in plain English and direct them to their data, like “What were the main reasons for customer churn in Europe last quarter?” and get immediate, narrated answers. This will make it easier than ever to get extensive insights.
The Shift to Data-as-a-Service (DaaS): DaaS is like Netflix for business data. It is a way of designing systems so that users can access data on demand through the cloud, no matter where that data is stored. This model, which is often supported by data marketplaces, removes the last obstacles to access, making it easy for teams to find, use, and share reliable data. This greatly increases the agility of the organization.
The Continued Focus on Data Governance and Security: As data becomes more essential to strategy, protecting it becomes even more important. Cyber threats become more advanced, regulations like GDPR set a global standard, and strong data governance is no longer an option. To build trust and make sure your company can last for a long time, your mature strategy must have strict rules for data quality, access management, privacy, and compliance.
Invite these innovations into your operations, and your business data analytics strategy is not merely up-to-date but future-proof as well.
The Future of Data: 3 Trends to Watch
| Augmented Analytics and AI | Data-as-a-Service (DaaS) | Data Governance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Idea | Ask questions in plain language, get answers instantly. | Access any data you need, anytime, like a utility. | As data becomes more valuable, its protection is paramount. |
| Business Impact |
|
|
|
Your Data Is Your Future
Your business data may hold the answers to your most critical questions about how to be more efficient, how customers react, and how to grow in the future. As we’ve explored together, turning raw, siloed data into a strategic revenue driver is the most innovation-friendly change your company can make. It is the best way to make a strong, competitive, and profitable business ready for possible turbulences in the future.
But you don’t have to go on this journey all by yourself. Getting help from an expert can make all the difference between a stalled project and the one that changes everything.
We invite you to take the next step if you’re ready to get the most out of the data you already have.
Reach out to GP Solutions today to set up a free consultation. We’ll help you examine your current data landscape and make a clear, actionable plan for turning your insights into your best source of income.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is business data analytics?
Business data analytics is the process of studying your company’s data to find worthwhile information that can aid with decision-making and performance. You need to use a variety of tools and methods to look at this kind of data, find patterns and trends, and figure out how to improve processes, solve problems, and reach your strategic goals.
2. What’s the very first step to starting a business data analytics project?
The first step is always strategic, not technical. It starts with deciding on a single, key business problem you want to solve or a specific question you need to answer. “Which of our customer segments is the most profitable over a five-year period?” and “What are the key drivers of employee churn in our sales department?” are two examples. Setting a clear business goal at the beginning of your analytics journey makes sure that you are always working toward real value.
3. Our data is messy and spread across multiple systems. Can we still use data analytics in business?
Yes. This is actually the most common point for almost every business to start. It’s a problem, but a treatable one. Data engineering is the first step in any promising analytics project. It involves cleaning up, consolidating, and integrating all of the messy, siloed data into one reliable source of truth. This is exactly where an experienced partner like GP Solutions can help, because we know how to build custom data pipelines that your systems need and deliver reliable data to your leadership.
4. Do we need to hire a team of data scientists immediately?
Not always. Many companies can get a great return on investment without having a full-time data scientist on staff at first. The most important thing is to know the difference between roles. A data analyst can find useful information using BI tools on data that is well-prepared. A data engineer builds the systems to provide such data. A data scientist usually designs complicated models that can predict the future. Oftentimes, the best way to go is to engage with a tech partner who has that engineering and advanced modeling experience, while you get the chance to ramp up efforts to train your in-house team.
5. How long does it take to see a return on investment (ROI)?
The timeline for ROI varies for each project, but a well-planned one adds value over time. You don’t have to wait months or years for a “big bang” result. Basic projects, such as building a unified sales and marketing dashboard (descriptive analytics), can provide you useful information and save time in just a few weeks. Building a model that can predict when customers will leave takes longer because it is more complicated. The best way to go about it is to make a phased roadmap that starts with high-impact “quick wins” to get things going and pay for later, more advanced projects.

















